Disclaimer
This platform provides ethical risk assessment for pathology foundation models (PFMs). The evaluation results are generated automatically based on the submitted models and available data. These results are provided for informational purposes only and do not constitute professional, medical, or legal advice.
By using this platform, you acknowledge and agree to the following:
- You will use this tool solely for research or authorized clinical workflow purposes.
- You will not redistribute model outputs or assessment results without proper approval.
- PFMs may produce probabilistic predictions that are not guaranteed to be correct in all cases.
- Final diagnostic, treatment, or management decisions must be made by certified healthcare professionals.
- The platform operators do not guarantee the completeness, accuracy, or suitability of the assessment results for any specific purpose.
- Use of the platform is at your own risk, and the operators are not liable for any direct or indirect consequences arising from the use of the results.
- Potential risks include, but are not limited to, misinterpretation of probabilistic predictions, incomplete evaluation of model behavior, and unexpected biases in the assessment.
- Users are responsible for ensuring compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and institutional policies when using model outputs.
By using this platform, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and accepted this disclaimer.
Ethical Aspects
Privacy Leakage, Clinical Reliability, Fairness.
Evaluation Tasks
26 datasets.
Organs
Span 8 types of cancer & Pan-cancer.
Image type
Whole slide images and Regions of interest.
The overview
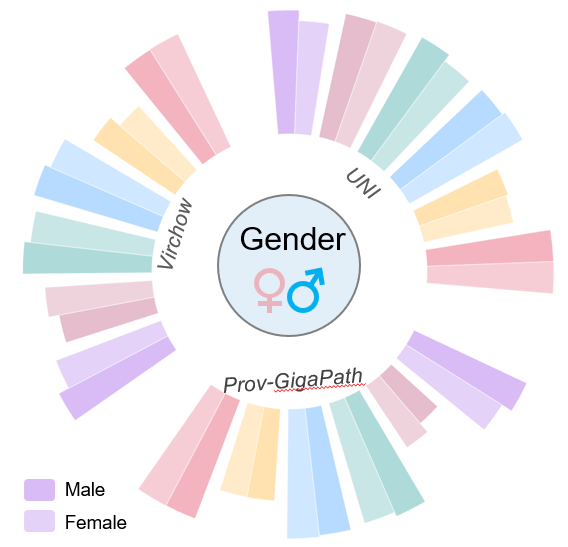
Privacy Leakage
Examining whether features embeddings generated by PFMs encode patient-sensitive information. Assessing the extent to which these information can be inferred from the feature embeddings.
Factors: Gender, Age, Race, Institution
Datasets: 9
Results:
PFM-generated feature embeddings encode patients' demographic information
PFM-generated feature embeddings encode patients' medical institution
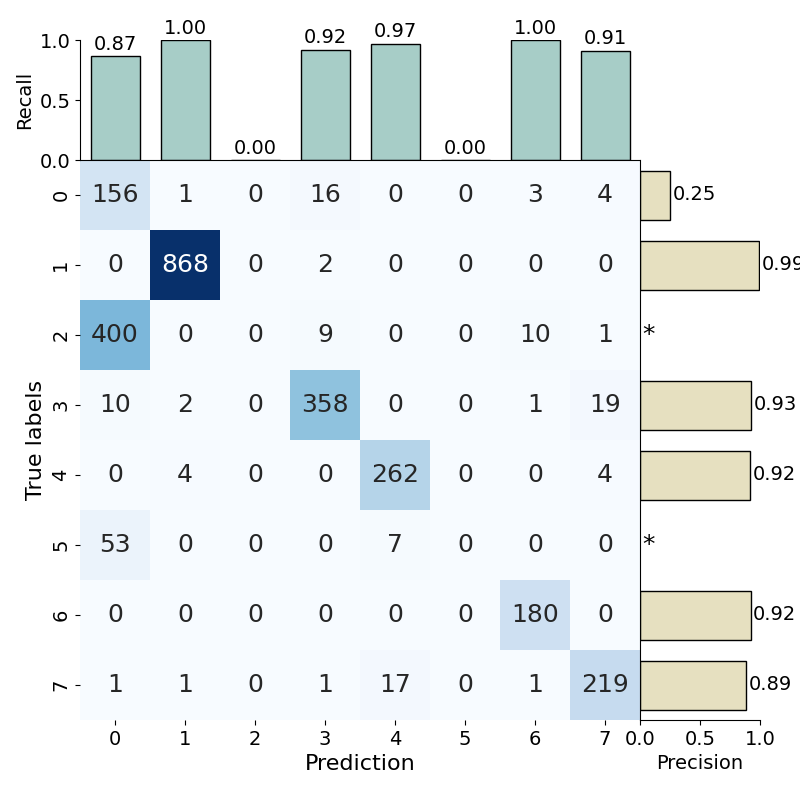
Clinical Reliability
Examining how non-diagnostic features affect the generalization ability and reliability of PFM-based downstream models. Evaluating their performance in OOD settings.
Diagnostic task: Patch classification/retrieval, WSI classification/survival analysis
Datasets: 9
Results:
Patch classification/retrieval performance declines in OOD settings.
WSI prediction performance declines in OOD settings.
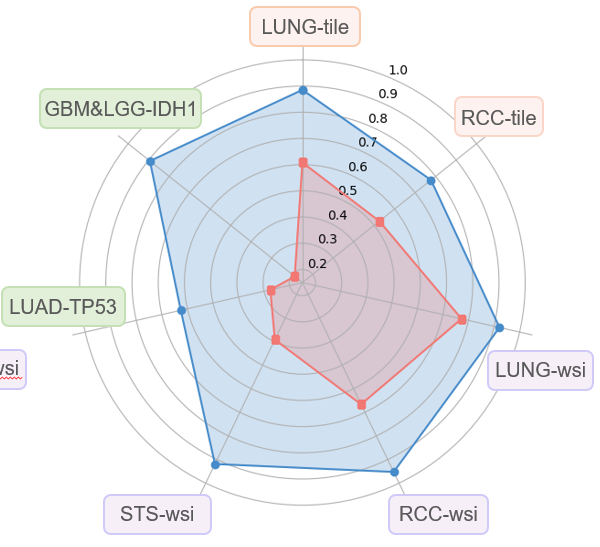
Fairness
Examining whether downstream models trained on PFM-derived feature embeddings maintain minimal performance disparities across different demographic or institutional subgroups
Diagnostic task: Patch/WSI classification
Datasets: 9
Results:
downstream models trained on PFM-derived features may exhibit fairness issues, raising concerns about their equitable applicability in real-world clinical environments.